History and Evolution of Spaghetti Models
![]()
Spaghetti models, also known as ensemble forecasts, emerged as a revolutionary approach in weather forecasting. Their origins can be traced back to the early 20th century when meteorologists began experimenting with statistical techniques to predict weather patterns. In the 1960s, with the advent of powerful computers, ensemble forecasting gained momentum, enabling the simulation of multiple weather scenarios simultaneously.
Advancements and Improvements
Over the decades, spaghetti models underwent significant advancements. In the 1970s, the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) developed the first operational ensemble prediction system, setting the stage for further refinement. The 1980s saw the introduction of Monte Carlo methods, enhancing the accuracy of ensemble forecasts by incorporating uncertainties in model inputs. In the 1990s, ensemble forecasting became widely adopted by major weather centers worldwide, leading to improved predictions of extreme weather events.
Historical Timeline
- 1920s: Statistical methods used in weather forecasting
- 1960s: Ensemble forecasting gains momentum with the advent of computers
- 1970s: ECMWF develops the first operational ensemble prediction system
- 1980s: Monte Carlo methods enhance ensemble forecast accuracy
li>1990s: Ensemble forecasting widely adopted by major weather centers
Applications and Use Cases of Spaghetti Models
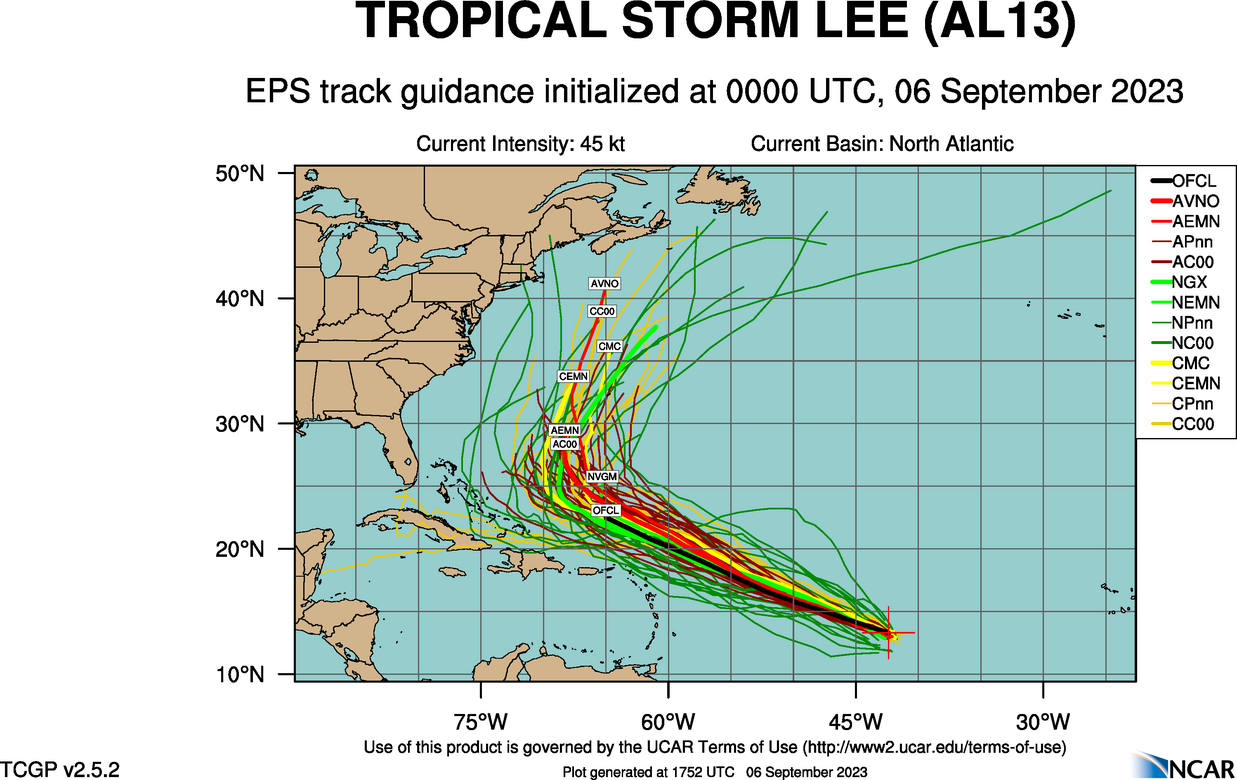
Spaghetti models have gained prominence in various fields, particularly in meteorology, climatology, and hydrology, where they are used to model complex systems and make predictions.
Meteorology
- Weather Forecasting: Spaghetti models are used to predict the path and intensity of hurricanes, tropical storms, and other weather events. They provide a range of possible outcomes, helping meteorologists assess the potential risks and make informed decisions.
- Climate Modeling: Spaghetti models are employed to simulate long-term climate patterns and predict future climate scenarios. They consider factors such as greenhouse gas emissions, ocean currents, and land-atmosphere interactions.
Climatology, Spaghetti models
- Climate Change Projections: Spaghetti models are used to project the potential impacts of climate change on temperature, precipitation, and sea levels. They provide a range of scenarios, helping policymakers and researchers understand the potential risks and develop adaptation strategies.
Hydrology
- Flood Forecasting: Spaghetti models are used to predict the likelihood and severity of floods. They consider factors such as rainfall intensity, soil moisture, and river discharge, providing valuable information for flood management and disaster preparedness.
- Water Resource Management: Spaghetti models are employed to simulate water availability and demand under different scenarios. They help water managers optimize water allocation and develop sustainable water use strategies.
Advantages of Spaghetti Models:
- Provide a range of possible outcomes, allowing for a more comprehensive assessment of risks and uncertainties.
- Can be used to simulate complex systems and incorporate a wide range of factors.
- Help identify potential extreme events and develop early warning systems.
Disadvantages of Spaghetti Models:
- Can be computationally expensive and require significant data.
- May produce a large number of simulations, making it challenging to interpret and communicate results.
- Relies on the accuracy of the underlying models and assumptions, which can introduce uncertainties.
Spaghetti models dey important for understanding weather patterns. Dem dey use spaghetti models to predict how hurricanes and typhoons go move. One of de most famous spaghetti models is de Beryl Barbados model. Dis model don help predict de path of many hurricanes and typhoons, including de recent Hurricane Ian.
Spaghetti models dey a powerful tool for meteorologists and dey help us to stay safe during hurricanes and typhoons.
Spaghetti models are a way to predict the path of a hurricane. They use a computer model to simulate the hurricane’s movement and produce a series of possible tracks. These tracks can help forecasters predict where the hurricane is likely to go and how strong it will be.
Hurricane Beryl , for example, was predicted to hit Florida, but the spaghetti models showed that it was likely to turn away before making landfall. This information helped officials prepare for the hurricane and evacuate people who were in its path.
Spaghetti models are an important tool for hurricane forecasting, and they can help save lives.